Webb Space Telescope, showcasing a region of space known as Pandora’s Cluster, or Abell 2744, features two galaxies. These galaxies are remarkable for their distance from Earth, being the second and fourth most distant galaxies ever observed, according to a team of researchers that recently scrutinised the image.
Webb first observed Abell 2744 in June 2022, including some 60,000 other light sources in a deep field of the cluster. Now, spectroscopic data from the galaxies revealed their superlative distance: about 33 billion light-years away, according to astronomers. Research describing the newfound characteristics of the ancient galaxies was published this week in the Astrophysical Journal Letters.
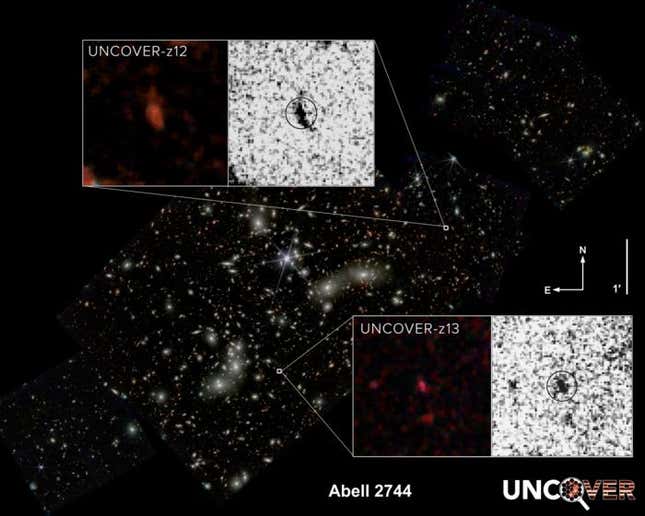
Ancient galaxies are generally point-like light sources in the eyes of space telescopes, but “one of ours appears elongated, almost like a peanut, and the other looks like a fluffy ball,” said Bingjie Wang, an astronomer at Penn State University and lead author of the recent paper.
“It is unclear if the difference in size is due to how the stars formed or what happened to them after they formed, but the diversity in the galaxy properties is really interesting.”
Webb Telescope’s similar findings
Astronomers have spied an intriguing phenomenon in the distant universe — a galaxy that closely resembles the Milky Way — and it’s challenging key theories on how galaxies evolve.
The faraway system, called ceers-2112, was spotted by an international team using the Webb Space Telescope.
Like our home galaxy, the newly discovered ceers-2112 is a barred spiral galaxy, and it’s now the most distant of its kind ever observed. The bar at the center of the structure is made of stars.
Ceers-2112 formed soon after the big bang created the universe (which is estimated to be 13.8 billion years old), and the galaxy’s distinct structure was already in place 2.1 billion years later.
“Finding ceers-2112 shows that galaxies in the early universe could be as ordered as the Milky Way,” said study coauthor Alexander de la Vega, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of California, Riverside, in a statement.
“This is surprising because galaxies were much more chaotic in the early universe and very few had similar structures to the Milky Way.”
About Webb Telescope
James Webb Telescope is perhaps the biggest and most complex piece of technology in the outer space. The design inspiration has to do a lot with when the Hubble Telescope was launched.
The Webb was launched on 25 December 2021 on an Ariane 5rocket from Kourou French Guinana. In January 2022 it arrived at its destination, a solar orbit near the Sun–Earth L2 Lagrange point, about 1.5 million kms (930,000 mi) from Earth. The telescope’s first image was released to the public on 11 July 2022.
James Webb is the collaborative product of many space organisations who have come together and prepared something which is “for the world, from the world”. National Aeronautic Space Agency (NASA), International Space Agency (ISA), European Space Agency (ESA), Canadian Space Agency (CSA), and The NASA Goddard Space Flight Centre ( GSFC) have together built this magnificent machinery. The entire operation is handled by John Hopkins University in Baltimore.
Conclusion
Webb Telescope is anticipated to be in the outer space for another decade. The amount of outer space information about the future of mankind can be in the hands of this telescope.
SpaceX is optimistic enough of launching a mission with NASA and other associated bodies to possibly shift the future of mankind to another planer as the threat of mankind vanishing away looms in the later future.
Does the world shift to any other planet or exo-planet or all of this is just a wet-blanket on the world?













